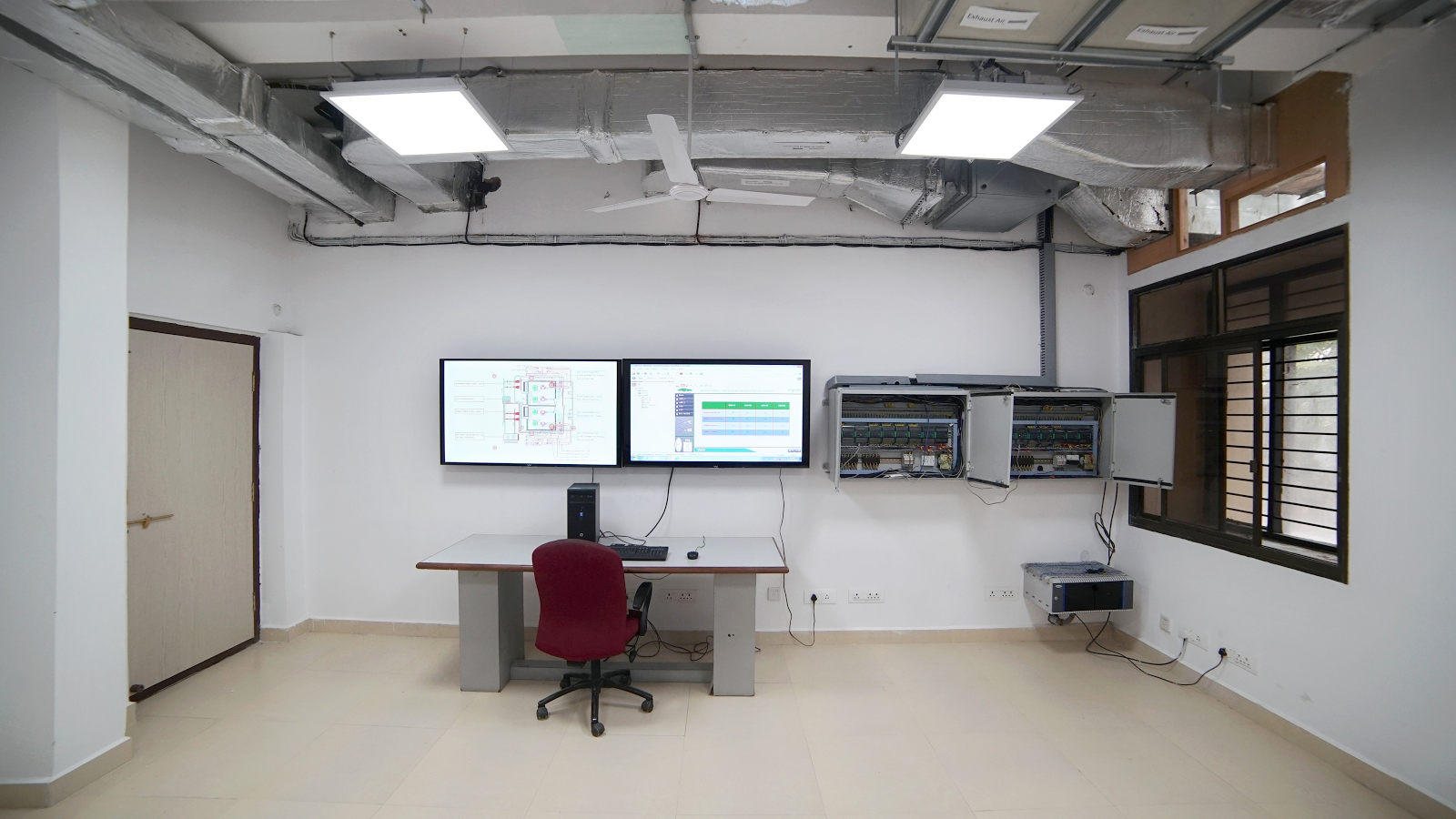
FDD Lab
Fault detection and diagnostic lab
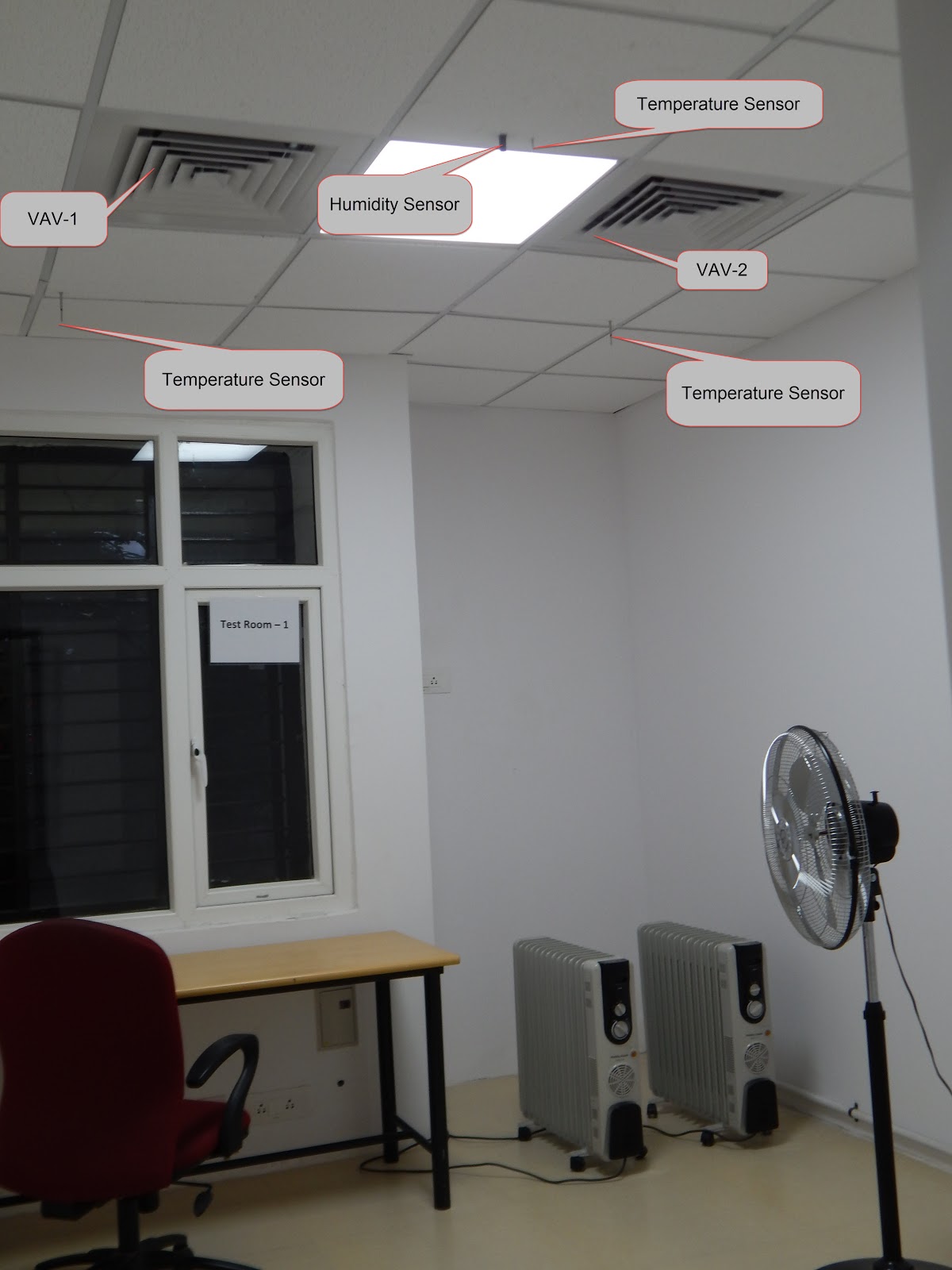
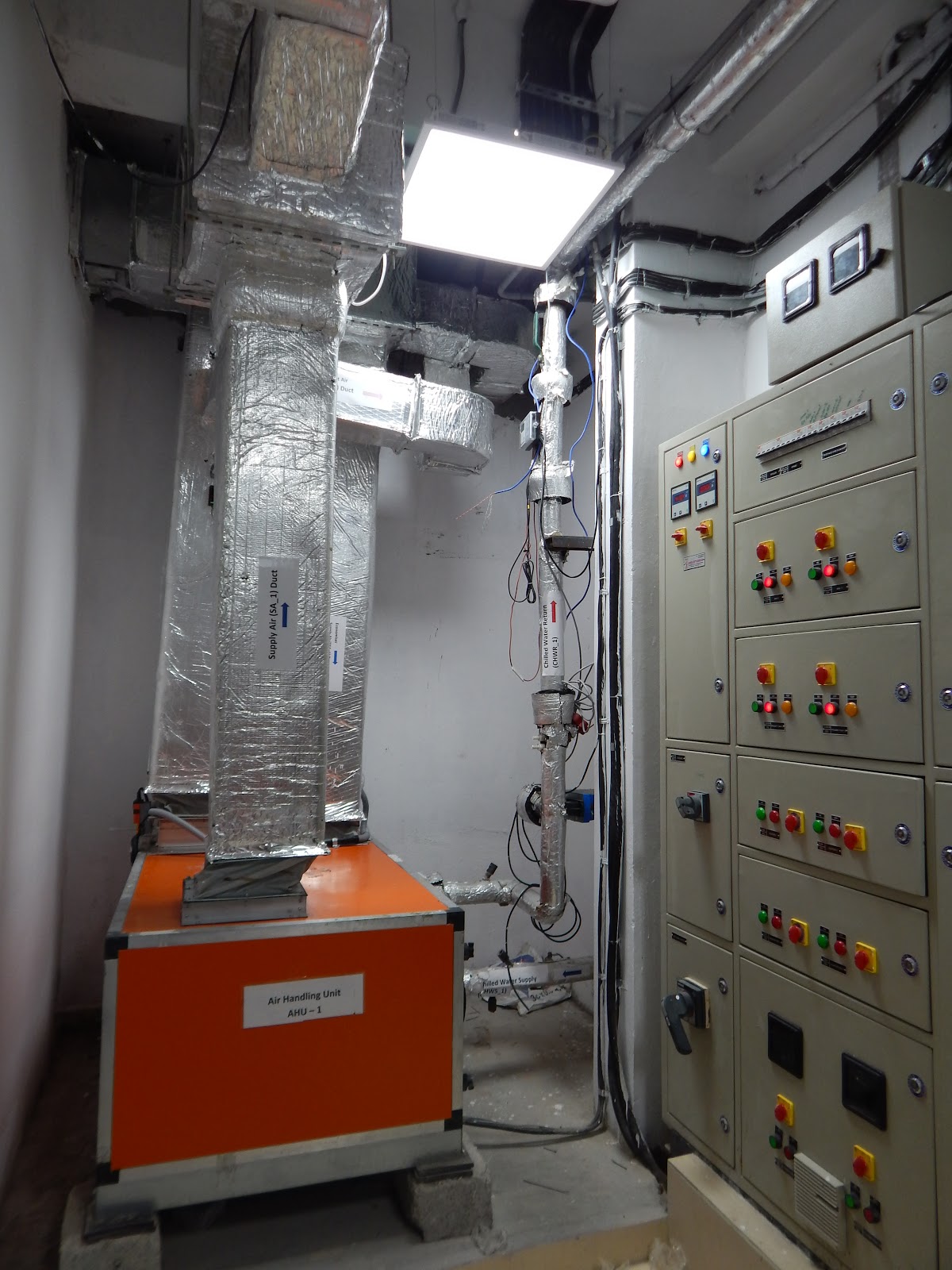
The purpose of establishing this facility is to develop, identify, and analyse faults in HVAC systems. This will help in development of effective HVAC FDD techniques for common faults such as variable air volume boxes, its dampers, actuators, controllers, airside economiser, AHU fan controllers, belts and bearings, valve leakage etc. Laboratory is consists of two identical side by side test chambers having 5.0 TR cooling capacity. Test chambers can be operated between 18°C and 30°C Indoor temperature range.

Cooling and Heating load calculation has been done using EnergyPlus simulation for all three outdoor conditions: summer, monsoon, and winter. For peak summer, air conditioning requirement for each test chamber is 3.5 TR and air supply flow required is 1145 CFM.
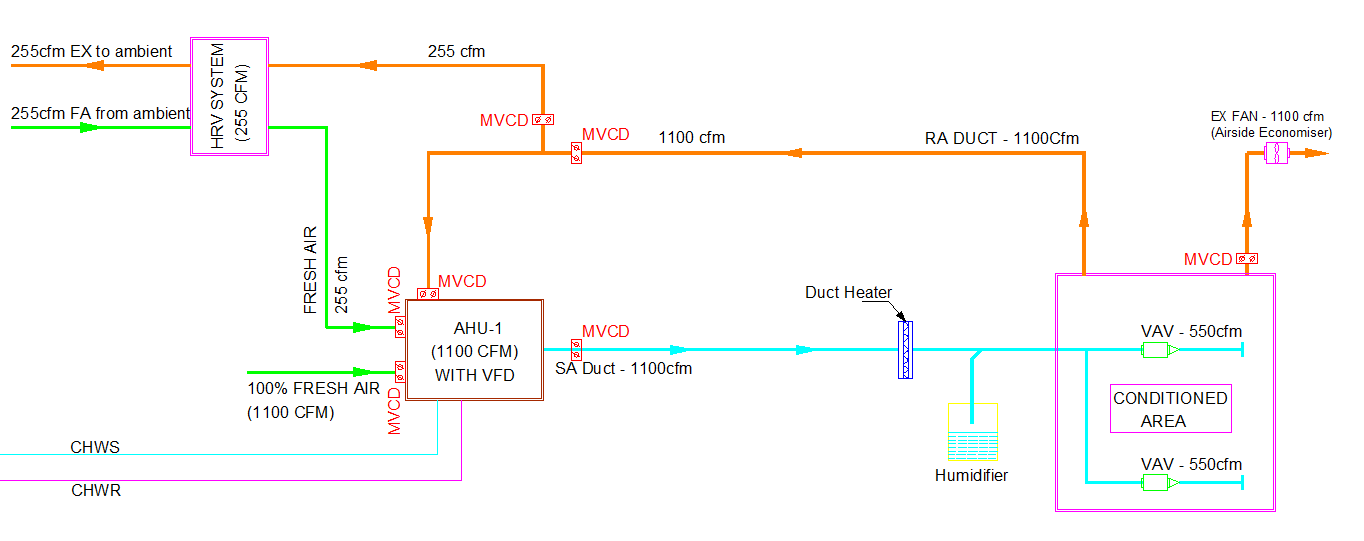
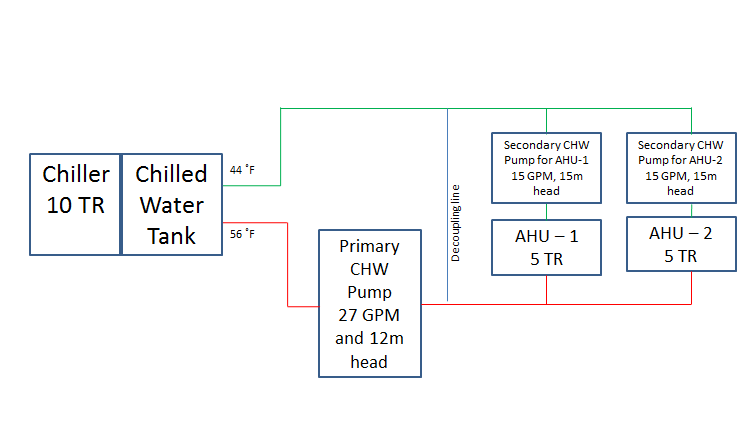


The implementation methodology of the faults identified is provided in Table 3. Faults related to Chiller is not considered for the analysis as sizing of the chiller is quite small and FDD techniques for the chiller are already well established.
Table 3 Faults, type and implementation method
| Fault | Type | Proposed implementation |
| VAV Faults | ||
| VAV damper stuck | Abrupt | Physical intervention: disconnect actuator input, position manually |
| VAV actuator fail | Abrupt | Physical intervention. |
| VAV leakage | Installation | Physical intervention: remove damper-blade seals |
| Controller hardware failure | Degradation | Install faulty controller |
| Air Handling Unit | ||
| Fan Faults | ||
| Unstable supply fan
controller |
Abrupt | Software override: change controller gain until oscillation
observed at low airflow rate |
| Slipping supply-fan belt | Degradation | Physical intervention: move fan motor to reduce tension in fan belt |
| Fan belts too tight | Degradation | Physical intervention: move fan motor to increase tension in fan belt |
| Dry bearings | Degradation | Physical intervention: Removal of lubrication |
| Case Faults | ||
| Improper AHU Drain connections | Installation | Physical intervention |
| Improper installation of fan motor | Installation | Physical intervention |
| Cooling Coil Faults | ||
| Leaking cooling coil valve | Degradation | Physical intervention: connect by-pass around control value |
| Reduced cooling-coil capacity (water side flow restriction) | Degradation | Physical intervention: restrict water flow to coil |
| Filter Faults | ||
| Blocked filter | Degradation | Physical intervention: Use of blocked filter |
| Pump Faults | ||
| Foreign material deposits | Degradation | Physical intervention: Use of old pumps |
| Corrosion | Degradation | Physical intervention: Use of old pumps |
| Oscillations | Abrupt | Physical intervention: Provide unstable foundation |
| Leakage | Abrupt | Physical intervention: Use of old pumps |
| Sensor Faults | ||
| Sensor offsets | Degradation | Use of faulty sensor |
| Positioning of Thermostats | Installation | By changing position of sensor |
| Duct Faults | ||
| Rusting in Duct | Degradation | Use of ducts with rust |
| Poor sensor placement in ducts | Installation | By altering position of sensor |
| Pipe Faults | ||
| Cleaning of chilled water strainers | Degradation | By installing used and un-cleaned strainer |
| Poor pipe insulation/ Condensation on pipe | Installation | By removing insulation |
| Air Side Economiser | ||
| Economiser Damper Failure | Abrupt | Physical intervention |
| Non-optimal economiser set-point | Degradation | By change of set point |
| Air temperature sensor failure | Abrupt | Use of faulty sensor |